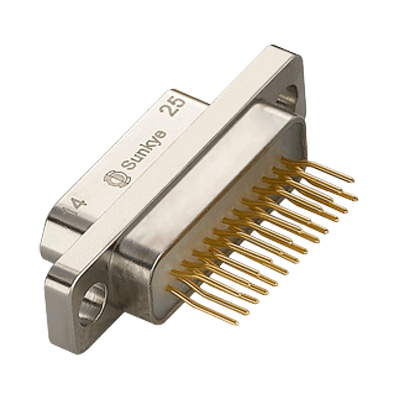
MIL-DTL-83513 Micro D Connectors
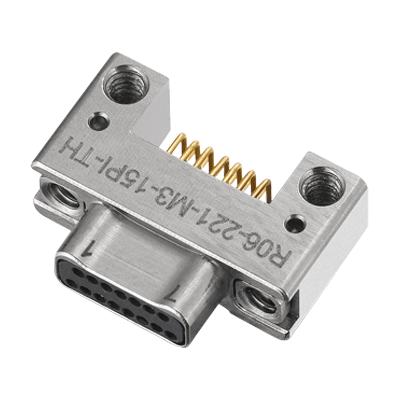
MIL-DTL-32139 Nano D Connectors
Discover more applications using Sunkye Connectors' solutions

Sunkye Connection Technologies provides a wide product portfolio with a complete interconnect solutions offering. Sunkye connectors and cables assemblies are complementary with Sunkye backshells and conduits.
 Nov 17, 2023
Future Development Trends of Circular Connectors
Nov 17, 2023
Future Development Trends of Circular Connectors
 Oct 13, 2020
Various Coaxial Connectors
Oct 13, 2020
Various Coaxial Connectors
 Dec 08, 2020
Some Knowledge about RJ45 Connector
Dec 08, 2020
Some Knowledge about RJ45 Connector
 Sep 14, 2019
Miniaturization Trend of Mil Connectors
Sep 14, 2019
Miniaturization Trend of Mil Connectors
 Jul 18, 2020
The Basic Structure of the Connector
Jul 18, 2020
The Basic Structure of the Connector
 Dec 29, 2019
Material Of Automotive Connectors
Dec 29, 2019
Material Of Automotive Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Connector
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Connector
 Jan 19, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Flat Cable Connector
Jan 19, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Flat Cable Connector
 Jan 18, 2021
Knowledge of FPC Connectors
Jan 18, 2021
Knowledge of FPC Connectors
 Oct 10, 2019
Types and Advantages of D-sub Connectors
Oct 10, 2019
Types and Advantages of D-sub Connectors
 Jan 16, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Strip Connector
Jan 16, 2020
Brief Introduction Of Strip Connector
 Nov 08, 2019
Miniaturization Development Technology Of Connector
Nov 08, 2019
Miniaturization Development Technology Of Connector
 Oct 07, 2020
How to Distinguish FFC Connector and FPC Connector
Oct 07, 2020
How to Distinguish FFC Connector and FPC Connector
 Nov 24, 2019
The Connector Applications Are Everywhere
Nov 24, 2019
The Connector Applications Are Everywhere
 Dec 02, 2019
Basic Structural Member Of Connector
Dec 02, 2019
Basic Structural Member Of Connector
 Jan 07, 2020
The Performance Of Automobile Connector
Jan 07, 2020
The Performance Of Automobile Connector
 Nov 23, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
Nov 23, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
 Jun 12, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (1)
Jun 12, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (1)
 Jun 25, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Datasheet
Jun 25, 2019
Sunkye Super Pin Datasheet
 Sep 13, 2020
Fusion of Connectors and Sensors
Sep 13, 2020
Fusion of Connectors and Sensors
 May 10, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (1)
May 10, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (1)
 Oct 13, 2023
Several Design Ideas for Electronic Connectors
Oct 13, 2023
Several Design Ideas for Electronic Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Everything You Need to Know: Type C
May 31, 2019
Everything You Need to Know: Type C
 Nov 17, 2022
Robotic Arm Works 7*24 in Manufacturing
Nov 17, 2022
Robotic Arm Works 7*24 in Manufacturing
 Jun 01, 2021
Functions and Advantages of Electrical Connectors
Jun 01, 2021
Functions and Advantages of Electrical Connectors
 Jan 04, 2021
The Structure and Material of Connectors
Jan 04, 2021
The Structure and Material of Connectors
 Oct 13, 2020
Selection Factors of RF Connectors
Oct 13, 2020
Selection Factors of RF Connectors
 Apr 13, 2020
Why is a Poor Connector Prone to Fire?
Apr 13, 2020
Why is a Poor Connector Prone to Fire?
 Sep 18, 2019
Definition of Mil Standard Connector
Sep 18, 2019
Definition of Mil Standard Connector
 Jun 18, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (1)
Jun 18, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (1)
 May 04, 2020
Automotive Connectors
May 04, 2020
Automotive Connectors
 Aug 09, 2021
What Are High Density Connectors?
Aug 09, 2021
What Are High Density Connectors?
 Jan 31, 2020
The Development Of D-sub Connectors
Jan 31, 2020
The Development Of D-sub Connectors
 Apr 28, 2020
How to Detect Medical Connectors
Apr 28, 2020
How to Detect Medical Connectors
 Oct 30, 2019
D Sub Connector Introduction
Oct 30, 2019
D Sub Connector Introduction
 May 13, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (2)
May 13, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors (2)
 Sep 21, 2021
Connection Mode and Purchase of Aerospace Connector
Sep 21, 2021
Connection Mode and Purchase of Aerospace Connector
 Oct 06, 2019
How Military Spec Connectors Work
Oct 06, 2019
How Military Spec Connectors Work
 Nov 01, 2021
Meet Sunkye at SEDEC 2020 Fair!
Nov 01, 2021
Meet Sunkye at SEDEC 2020 Fair!
 Apr 04, 2020
The Material of the Connector
Apr 04, 2020
The Material of the Connector
 Feb 15, 2021
The Power Capacity of RF Coaxial Connectors
Feb 15, 2021
The Power Capacity of RF Coaxial Connectors
 Aug 02, 2020
Electrical Performance of Connector
Aug 02, 2020
Electrical Performance of Connector
 Oct 02, 2023
MEET SUNKYE AT ADIPEC 2023 FAIR
Oct 02, 2023
MEET SUNKYE AT ADIPEC 2023 FAIR
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye at Expo Electronica 2014, Moscow
May 31, 2019
Sunkye at Expo Electronica 2014, Moscow
 Jun 06, 2019
Alloy 52 UNS N14052 Material Report
Jun 06, 2019
Alloy 52 UNS N14052 Material Report
 Jul 21, 2020
What is a Military Specification Circular Connector?
Jul 21, 2020
What is a Military Specification Circular Connector?
 Aug 19, 2024
Can a Connector Withstand Temperatures Up to 500°C?
Aug 19, 2024
Can a Connector Withstand Temperatures Up to 500°C?
 Jun 24, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (3)
Jun 24, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (3)
 May 27, 2021
The Importance of Connectors in Electrical Equipment
May 27, 2021
The Importance of Connectors in Electrical Equipment
 Dec 17, 2019
Interconnection Level Of Connector
Dec 17, 2019
Interconnection Level Of Connector
 Mar 29, 2020
Demand for Heavy Truck Connectors Increases
Mar 29, 2020
Demand for Heavy Truck Connectors Increases
 Nov 29, 2019
Importance Of Connectors
Nov 29, 2019
Importance Of Connectors
 Sep 06, 2019
Polytetrafluoroethylene-PTFE
Sep 06, 2019
Polytetrafluoroethylene-PTFE
 Jul 17, 2024
MEET SUNKYE AT ONS 2024
Jul 17, 2024
MEET SUNKYE AT ONS 2024
 Dec 23, 2019
Technical Principles Of Connectors
Dec 23, 2019
Technical Principles Of Connectors
 Oct 31, 2019
The Introduction Of SMT
Oct 31, 2019
The Introduction Of SMT
 Apr 07, 2020
Market Status of Miniature Connectors
Apr 07, 2020
Market Status of Miniature Connectors
 Dec 14, 2019
Naming Of Connectors
Dec 14, 2019
Naming Of Connectors
 Mar 08, 2020
Sunkye: Safety, Innovation, Reliability
Mar 08, 2020
Sunkye: Safety, Innovation, Reliability
 Nov 05, 2019
Wearable Connectors Tend to be Miniaturization
Nov 05, 2019
Wearable Connectors Tend to be Miniaturization
 Sep 20, 2019
Strictness of Military/Aerospace Specifications
Sep 20, 2019
Strictness of Military/Aerospace Specifications
 Sep 08, 2019
What are Avionics Connectors?
Sep 08, 2019
What are Avionics Connectors?
 Nov 04, 2019
How Military Connectors Work
Nov 04, 2019
How Military Connectors Work
 Oct 19, 2021
Subsea Connector needs a new revolution
Oct 19, 2021
Subsea Connector needs a new revolution
 Aug 15, 2023
Extreme Conditions Bring up Hermetic Connectors
Aug 15, 2023
Extreme Conditions Bring up Hermetic Connectors
 Jan 25, 2021
The Analysis of Connector Electroplating Problems
Jan 25, 2021
The Analysis of Connector Electroplating Problems
 Dec 22, 2020
The Transient Interruption Detection of Connectors
Dec 22, 2020
The Transient Interruption Detection of Connectors
 Jan 13, 2020
Overall Performance Parameters Of Connector
Jan 13, 2020
Overall Performance Parameters Of Connector
 Jul 09, 2020
The Importance of Connectors in Medical Equipment
Jul 09, 2020
The Importance of Connectors in Medical Equipment
 Dec 01, 2021
Connectors' Revolution of 1000km off The Earth
Dec 01, 2021
Connectors' Revolution of 1000km off The Earth
 Jan 04, 2023
Four Connection Methods of Circular Connectors
Jan 04, 2023
Four Connection Methods of Circular Connectors
 Sep 28, 2019
Development Trend of Miniature Connectors Technology
Sep 28, 2019
Development Trend of Miniature Connectors Technology
 Jul 15, 2020
Classification of Connectors
Jul 15, 2020
Classification of Connectors
 Aug 09, 2019
Development of Micro Connector
Aug 09, 2019
Development of Micro Connector
 Nov 17, 2020
Selection Factors for SMA Connectors
Nov 17, 2020
Selection Factors for SMA Connectors
 Aug 01, 2022
Connectors Make Sensors Work Well on Equipment
Aug 01, 2022
Connectors Make Sensors Work Well on Equipment
 Nov 03, 2019
Some Solutions For Poor Terminal Pressing
Nov 03, 2019
Some Solutions For Poor Terminal Pressing
 Mar 20, 2020
Connector Quality Test Type
Mar 20, 2020
Connector Quality Test Type
 Nov 14, 2019
How To Choose The Right Connector
Nov 14, 2019
How To Choose The Right Connector
 Feb 25, 2020
How to Choose the Right Medical Connector
Feb 25, 2020
How to Choose the Right Medical Connector
 Jul 08, 2021
Structural Analysis of Aerospace Connector
Jul 08, 2021
Structural Analysis of Aerospace Connector
 Sep 08, 2022
How Does Environment Temperature Affect Connectors?
Sep 08, 2022
How Does Environment Temperature Affect Connectors?
 Jul 06, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (2)
Jul 06, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (2)
 Apr 25, 2020
The Second Generation Circular Military Connector
Apr 25, 2020
The Second Generation Circular Military Connector
 Oct 06, 2020
Description of Pogo Pin Connectors
Oct 06, 2020
Description of Pogo Pin Connectors
 Nov 02, 2021
MEET SUNKYE AT SAHA EXPO 2021 FAIR!
Nov 02, 2021
MEET SUNKYE AT SAHA EXPO 2021 FAIR!
 Nov 10, 2020
Applications and Characteristics of BNC Connectors
Nov 10, 2020
Applications and Characteristics of BNC Connectors
 Nov 01, 2019
Five Common Features of USB Connector
Nov 01, 2019
Five Common Features of USB Connector
 Feb 10, 2020
The Function And Prospect Of Medical Connector
Feb 10, 2020
The Function And Prospect Of Medical Connector
 Jan 01, 2020
Development Trend Of Automobile Connector In China
Jan 01, 2020
Development Trend Of Automobile Connector In China
 Jan 03, 2024
Connector — A Big Player in Your Supply Chain
Jan 03, 2024
Connector — A Big Player in Your Supply Chain
 Feb 13, 2020
Connection Between Brain And Machine
Feb 13, 2020
Connection Between Brain And Machine
 May 31, 2019
TWIST PIN: THE LIGHTSPOT OF SUNKYE
May 31, 2019
TWIST PIN: THE LIGHTSPOT OF SUNKYE
 Oct 01, 2020
Structure and Material of Waterproof Connector
Oct 01, 2020
Structure and Material of Waterproof Connector
 Sep 25, 2020
Related Knowledge of SMA RF Connector
Sep 25, 2020
Related Knowledge of SMA RF Connector
 May 31, 2019
SUNKYE will Release Type C Project on October
May 31, 2019
SUNKYE will Release Type C Project on October
 Jun 15, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (2)
Jun 15, 2020
7 Tips for Connector Design (2)
 Nov 10, 2019
The Future Trend Of Automobile Connector
Nov 10, 2019
The Future Trend Of Automobile Connector
 Jan 11, 2021
How to Select Connectors for Hardware Design
Jan 11, 2021
How to Select Connectors for Hardware Design
 Feb 19, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors
Feb 19, 2020
Reliability of Aerospace Electrical Connectors
 Jul 30, 2019
Market Status of Micro Connectors
Jul 30, 2019
Market Status of Micro Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Will Postpone the Release of USB 3.1 Type C
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Will Postpone the Release of USB 3.1 Type C
 Sep 24, 2019
Notes for Welding D Type Connector
Sep 24, 2019
Notes for Welding D Type Connector
 Sep 19, 2020
The Necessity of Waterproof Connectors
Sep 19, 2020
The Necessity of Waterproof Connectors
 Oct 18, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
Oct 18, 2022
Hermetic Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
 May 31, 2019
Features of Type C
May 31, 2019
Features of Type C
 Jun 27, 2020
Crimping and Welding of Military Connectors
Jun 27, 2020
Crimping and Welding of Military Connectors
 Sep 02, 2019
Four Processes of Producing Connectors
Sep 02, 2019
Four Processes of Producing Connectors
 Jan 25, 2020
Four Types Of Industrial Electrical Connectors
Jan 25, 2020
Four Types Of Industrial Electrical Connectors
 Oct 20, 2020
The Failure Mechanism of Connectors
Oct 20, 2020
The Failure Mechanism of Connectors
 Jul 17, 2020
Sunkye Market Matrix
Jul 17, 2020
Sunkye Market Matrix
 Nov 09, 2019
Introduction To Connector Knowledge
Nov 09, 2019
Introduction To Connector Knowledge
 Dec 01, 2020
How to Improve the Reliability of RF Connectors
Dec 01, 2020
How to Improve the Reliability of RF Connectors
 Apr 01, 2020
Connectors for Special Applications
Apr 01, 2020
Connectors for Special Applications
 Dec 08, 2019
Connection Methods Of The Connector
Dec 08, 2019
Connection Methods Of The Connector
 Dec 05, 2019
Disassembly Tools For Automotive Connectors
Dec 05, 2019
Disassembly Tools For Automotive Connectors
 Aug 02, 2021
Introduction to Vehicle Connectors
Aug 02, 2021
Introduction to Vehicle Connectors
 Dec 26, 2019
How To Classify Industrial Connectors
Dec 26, 2019
How To Classify Industrial Connectors
 Nov 06, 2019
Connector Classification
Nov 06, 2019
Connector Classification
 Feb 07, 2020
The Rapidly Growing Market For Medical Connectors
Feb 07, 2020
The Rapidly Growing Market For Medical Connectors
 Nov 15, 2019
How To Make High-Quality Connector
Nov 15, 2019
How To Make High-Quality Connector
 Dec 22, 2024
Specialty Gas Connectors for Niche Applications
Dec 22, 2024
Specialty Gas Connectors for Niche Applications
 Nov 10, 2020
The Manufacturing Process of Electronic Connectors
Nov 10, 2020
The Manufacturing Process of Electronic Connectors
 Sep 04, 2019
Market Profile of Micro PCB Connectors
Sep 04, 2019
Market Profile of Micro PCB Connectors
 Aug 07, 2019
A Revolution in Connector Technology
Aug 07, 2019
A Revolution in Connector Technology
 Jan 28, 2020
The Connector Industry Is Booming
Jan 28, 2020
The Connector Industry Is Booming
 Nov 12, 2019
Production Technology of Connector
Nov 12, 2019
Production Technology of Connector
 Sep 26, 2019
Market Status of Micro Miniature Connectors
Sep 26, 2019
Market Status of Micro Miniature Connectors
 Jul 12, 2020
Introduction to the Connector
Jul 12, 2020
Introduction to the Connector
 Sep 12, 2019
Reliable Connectors Are the Secret of UAV Success
Sep 12, 2019
Reliable Connectors Are the Secret of UAV Success
 Jun 21, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (2)
Jun 21, 2020
Application of Military Electrical Connectors (2)
 Aug 03, 2019
Connector D Type
Aug 03, 2019
Connector D Type
 Apr 22, 2020
Production Process of Connector Contacts
Apr 22, 2020
Production Process of Connector Contacts
 Jul 03, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (1)
Jul 03, 2020
Manual Assembly of Connectors (1)
 Dec 11, 2019
The Main Classification Of Crimp Connection
Dec 11, 2019
The Main Classification Of Crimp Connection
 Nov 03, 2020
The Guide for Selecting Electrical Connectors
Nov 03, 2020
The Guide for Selecting Electrical Connectors
 May 31, 2019
Sunkye Type C 10Gbps Test on April
May 31, 2019
Sunkye Type C 10Gbps Test on April
 Oct 25, 2024
Harnessing Wind Energy: Sustainable Power Solutions
Oct 25, 2024
Harnessing Wind Energy: Sustainable Power Solutions
 Feb 08, 2021
Four Attention Points in Using Power Connectors
Feb 08, 2021
Four Attention Points in Using Power Connectors
 Sep 28, 2021
Correct Use and Safety of Avionics Connectors
Sep 28, 2021
Correct Use and Safety of Avionics Connectors
 Jan 22, 2020
Differences Between Connector And Terminal
Jan 22, 2020
Differences Between Connector And Terminal
 Nov 11, 2019
Brief Introduction Of Automobile Connector
Nov 11, 2019
Brief Introduction Of Automobile Connector
GET IN TOUCH
MIL-DTL-32139 Nano D Connectors
 English
English  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  русский
русский  Türkçe
Türkçe  Svenska
Svenska  Nederland
Nederland